Introduction
The insurance landscape in the United States has undergone significant transformations, with the introduction of insurance exchanges playing a pivotal role. These exchanges serve as marketplaces where individuals and businesses can explore, compare, and purchase various insurance plans. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the intricacies of insurance exchanges in the USA, exploring their purpose, key features, and the impact they have on the accessibility of insurance coverage.
Evolution of Insurance Exchanges
1. Historical Context:
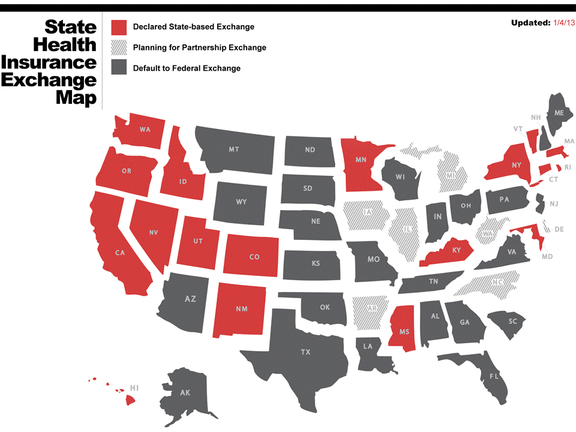
The concept of insurance exchanges gained prominence with the passage of the Affordable Care Act (ACA) in 2010. The ACA aimed to enhance the accessibility and affordability of health insurance, and insurance exchanges were established as a fundamental component of this healthcare reform.
2. Types of Insurance Exchanges:
There are two primary types of insurance exchanges in the USA:
- Health Insurance Exchanges (Marketplaces): These are platforms where individuals and families can shop for and enroll in health insurance plans. The Health Insurance Marketplace is a key feature of the ACA, offering a range of plans with varying coverage levels and costs.
- Insurance Marketplaces for Other Coverage Types: In addition to health insurance exchanges, there are marketplaces that cater to other types of insurance, such as property and casualty insurance. These platforms provide a centralized space for individuals and businesses to explore diverse coverage options.
The Role of Health Insurance Exchanges
1. Enhancing Access to Health Coverage:
One of the primary goals of health insurance exchanges is to broaden access to health coverage. By centralizing various insurance plans in a marketplace, individuals and families can easily compare options, determine eligibility for subsidies, and choose plans that align with their healthcare needs.
2. Facilitating Price Transparency:
Insurance exchanges promote price transparency by providing clear information about the costs and benefits of different plans. This transparency empowers consumers to make informed decisions based on their budget and the level of coverage they require.
3. Subsidies and Financial Assistance:
Many individuals and families may be eligible for subsidies and financial assistance through health insurance exchanges. These subsidies aim to make health coverage more affordable, particularly for those with lower incomes. Eligibility is often determined based on factors such as income and household size.
Key Features of Insurance Exchanges
1. Open Enrollment Periods:
Health insurance exchanges typically operate on a schedule of open enrollment periods. During these specified times, individuals can enroll in or make changes to their health insurance plans. Outside of open enrollment, special circumstances such as qualifying life events may allow for enrollment or plan changes.
2. Qualified Health Plans (QHPs):
Insurance plans offered through health insurance exchanges must meet certain criteria to be classified as Qualified Health Plans (QHPs). These criteria ensure that the plans provide essential health benefits, meet minimum standards, and comply with regulations set forth by the ACA.
3. Essential Health Benefits:
Health insurance plans available on exchanges are required to cover essential health benefits, including services such as preventive care, prescription drugs, maternity care, and mental health services. This guarantees that people can obtain a wide range of healthcare treatments.
4. Metallic Tier System:
Health insurance plans on exchanges are often categorized into metallic tiers, including Bronze, Silver, Gold, and Platinum. These tiers represent the level of coverage, with Bronze offering the least coverage and Platinum providing the highest level of coverage. The tier system allows individuals to choose plans based on their specific needs and budget.
Beyond Health Insurance: Other Insurance Exchanges

1. Property and Casualty Insurance Exchanges:
While health insurance exchanges are prominent, there are also exchanges dedicated to other types of insurance, such as property and casualty insurance. These platforms offer a centralized marketplace for individuals and businesses to explore options for coverage related to property, liability, and other non-health-related risks.
2. Business and Commercial Insurance Exchanges:
Businesses, both small and large, can benefit from insurance exchanges that focus on commercial coverage. These exchanges provide a streamlined process for businesses to assess and purchase insurance plans tailored to their specific industry, size, and risk profile.
Challenges and Considerations
1. Navigating Complexity:
The insurance landscape, with its diverse plans and regulations, can be complex. Individuals and businesses may find it challenging to navigate the various options available on exchanges. Seeking assistance from insurance brokers or utilizing online tools provided by exchanges can help simplify the process.
2. Changes in Policies and Regulations:
Insurance exchanges are influenced by changes in policies and regulations. Shifts in government policies can impact the structure of exchanges, eligibility criteria, and the availability of subsidies. Staying informed about these changes is crucial for individuals and businesses relying on insurance exchanges for coverage.
3. Limited Enrollment Periods:
The structured open enrollment periods for health insurance exchanges mean that individuals must plan their enrollment carefully. Missing these periods may limit options for obtaining coverage, emphasizing the importance of timely decision-making.
The Future of Insurance Exchanges
1. Technological Advancements:
The future of insurance exchanges is likely to be shaped by technological advancements. Online platforms, mobile applications, and data analytics are expected to play an increasing role in enhancing the user experience, facilitating efficient enrollment processes, and improving accessibility.
2. Expansion of Coverage Options:
As insurance exchanges evolve, there may be an expansion of coverage options beyond traditional health and commercial insurance. Innovations in insurance products and the inclusion of emerging coverage needs could broaden the scope of offerings on exchanges.
3. Public Awareness and Education:
Increasing public awareness and education about insurance exchanges will be essential for maximizing their impact. Efforts to inform individuals, businesses, and communities about the benefits, subsidies, and coverage options available can contribute to a more informed and empowered population.
Conclusion
Insurance exchanges in the USA represent a transformative approach to accessing and purchasing insurance coverage. From health insurance exchanges that address the essential healthcare needs of individuals to marketplaces catering to various other insurance types, these platforms aim to enhance accessibility, transparency, and affordability. Navigating the insurance landscape through exchanges requires careful consideration of individual needs, policy features, and eligibility criteria. As technology advances and the regulatory landscape evolves, the role of insurance exchanges is likely to continue expanding, contributing to a more inclusive and efficient insurance marketplace for individuals and businesses alike.




