
Introduction
Loan amortisation, a fundamental financial concept, plays a crucial role in the world of lending and borrowing. This method is employed to gradually pay off debts, such as mortgages or car loans, through scheduled payments covering both principal and interest. This systematic repayment process ensures that borrowers repay the entire loan amount by the end of the loan term. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of loan amortisation, exploring its mechanics, benefits, and potential pitfalls.
Mechanics of Loan Amortisation:
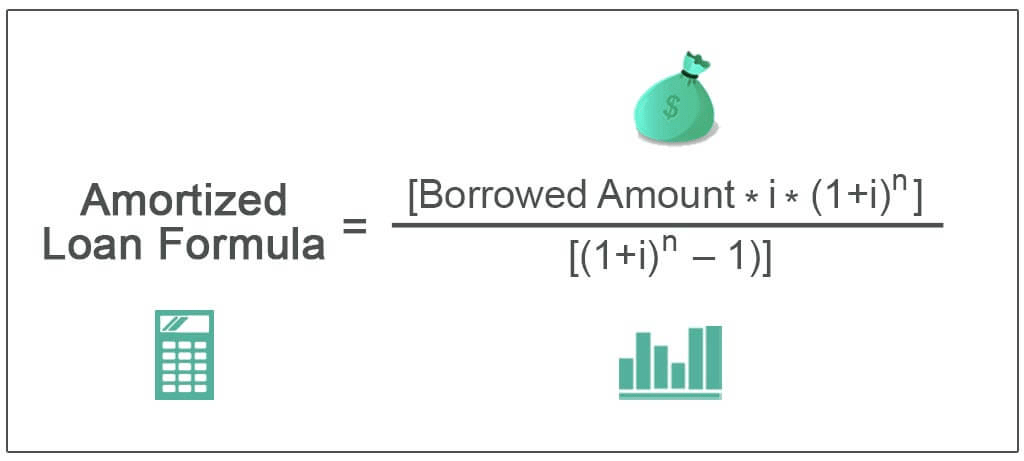
At the core of loan amortisation lies the principle of spreading the total loan amount over a set period, typically in the form of monthly payments. Each instalment consists of two components: principal and interest. The principal is the original loan amount, while the interest represents the cost of borrowing.
In the early stages, a significant portion of each payment goes towards paying off interest, with a smaller fraction dedicated to reducing the principal. As time progresses, the ratio shifts, with a larger portion of the payment allocated to the principal, leading to a gradual decrease in the outstanding balance. This process continues until the loan is fully repaid.
Benefits of Loan Amortisation:
1. Predictable Payments: One of the key advantages of loan amortisation is the predictability it offers borrowers. With fixed monthly payments, individuals can plan their budgets effectively, knowing exactly how much they need to set aside each month to meet their financial obligations.
2. Builds Equity: For mortgages, loan amortisation contributes to building equity in the home. Equity is the difference between the property’s market value and the outstanding mortgage balance. As borrowers make principal payments, their ownership stake in the property increases.
3. Interest Reduction: Over time, the interest component of the monthly payment decreases as the principal is paid down. This results in a lower overall interest cost compared to non-amortising loans or loans with variable interest rates.
Potential Pitfalls and Considerations:

1. Front-Loaded Interest: In the initial years of an amortising loan, a significant portion of each payment goes toward interest, which can be disheartening for borrowers. It means that the outstanding balance decreases more slowly during the early stages of the loan.
2. Prepayment Penalties: Some loan agreements impose prepayment penalties if borrowers decide to pay off their loans before the scheduled term. This can be a significant drawback for individuals who wish to accelerate their debt repayment.
Loan Amortisation in Real Estate:
One of the most common applications of loan amortisation is in real estate, where mortgages are prevalent. When individuals purchase homes, they often opt for a mortgage to finance the purchase. Mortgage loans are typically structured with a fixed interest rate and a predetermined repayment period, commonly 15 or 30 years.
In real estate, the amortisation process is particularly beneficial for homeowners. As they make regular mortgage payments, they not only service the debt but also build equity in their homes. This equity can be tapped into through various means, such as home equity loans or lines of credit.
Loan Amortisation in Business:

Beyond personal finance and real estate, is a critical concept in the business world. Companies often take out loans to finance capital expenditures, expansion projects, or to manage cash flow. Understanding loan amortisation is essential for business owners and financial managers as it directly impacts the company’s financial statements and cash flow projections.
Conclusion:
Loan amortisation is a fundamental financial concept that underpins various aspects of personal and business finance. Whether it’s buying a home, financing a car, or funding a business expansion, the principles of loan amortisation shape the way individuals and companies manage and repay their debts.




One Comment on “Loan Amortisation: A Comprehensive Guide”