
Introduction:
In the intricate tapestry of financial planning, life insurance emerges as a critical thread that weaves together the protection of loved ones and the assurance of a secure future. This comprehensive guide aims to unravel the complexities surrounding life insurance, shedding light on its importance, types, considerations, and the pivotal role it plays in safeguarding the financial well-being of individuals and their families.
The Importance of Life Insurance:
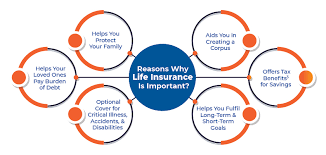
1. Financial Protection for Loved Ones:
- At its core, life insurance serves as a safety net for loved ones in the event of the policyholder’s demise. By providing a financial cushion, it ensures that dependents are not burdened with the economic challenges that can arise from the loss of the primary breadwinner.
2. Debt Repayment and Expenses:
- can play a crucial role in settling outstanding debts and covering various expenses. From mortgages to education loans, the proceeds from a policy can be utilized to alleviate financial burdens, allowing surviving family members to maintain their quality of life.
3. Estate Planning:
- Life insurance is often a key component of estate planning. It provides a means to pass on assets to heirs, beneficiaries, or charitable causes. This strategic use of life insurance can facilitate the smooth transfer of wealth and minimize potential tax implications.
4. Business Continuity:
- For business owners, life insurance is a tool for ensuring the continuity of operations in the face of unexpected events. It can be utilized to fund buy-sell agreements, repay business debts, or provide a financial cushion to sustain the business in the absence of a key figure.
Types of Life Insurance:
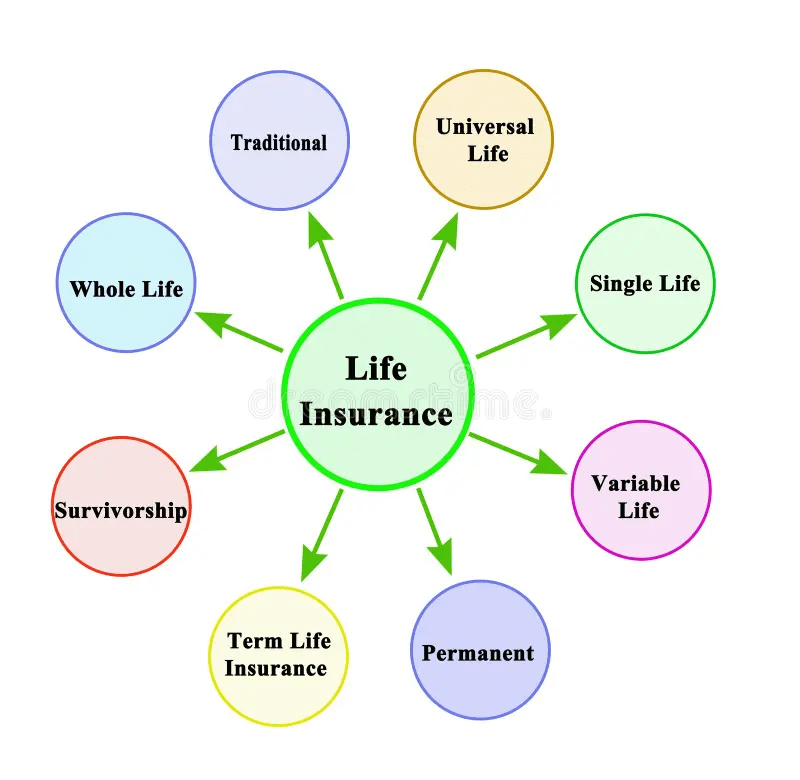
1. Term Life Insurance:
- Term provides coverage for a specific term, typically ranging from 10 to 30 years. If the policyholder passes away during the term, the beneficiaries receive the death benefit. Term is known for its affordability and straightforward structure.
2. Whole Life Insurance:
- Whole offers coverage for the entire lifetime of the policyholder. It combines a death benefit with a cash value component that accumulates over time. Whole life policies tend to have higher premiums but provide a lifelong safety net.
3. Universal Life Insurance:
- Universal is a flexible form of coverage that allows policyholders to adjust their premiums and death benefits. It also includes a cash value component that earns interest based on prevailing market rates. This flexibility makes it attractive for those seeking a customizable policy.
4. Variable Life Insurance:
- Variable allows policyholders to invest the cash value component in a variety of investment options such as stocks and bonds. The policy’s cash value and death benefit can fluctuate based on the performance of the chosen investments.
Considerations When Choosing Life Insurance:

1. Assessing Coverage Needs:
- The first step in selecting is to assess the coverage needs. Consider factors such as outstanding debts, future expenses (e.g., education costs), and the financial needs of dependents. This evaluation forms the basis for determining the appropriate coverage amount.
2. Understanding Term vs. Permanent Insurance:
- Decide between term and permanent life insurance based on your specific needs. Term insurance may be suitable for those seeking coverage for a specific period, while permanent insurance provides lifelong protection with additional features.
3. Evaluating Premium Affordability:
- Affordability is a key factor when selecting . Evaluate your budget and choose a policy with premiums that are manageable over the long term. Be cautious not to overextend financially for coverage that exceeds your needs.
4. Considering Additional Riders:
- policies often offer additional riders or endorsements that provide enhanced coverage. Common riders include accelerated death benefit riders, which allow for the early payout of a portion of the death benefit in the case of a terminal illness, and waiver of premium riders, which waive premiums in the event of disability.
5. Reviewing Policy Exclusions and Limitations:

- Thoroughly review the policy’s exclusions and limitations. Understand the circumstances under which the policy may not pay out, such as suicide within the first two years of the policy or engaging in high-risk activities.
The Application Process and Underwriting:
1. Application Submission:
- The application process typically begins with the submission of an application. This involves providing personal information, medical history, lifestyle details, and financial data.
2. Medical Examination:
- Many life insurance policies require a medical examination as part of the underwriting process. This examination may include blood tests, urine tests, and other health assessments to evaluate the applicant’s overall health.




Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!